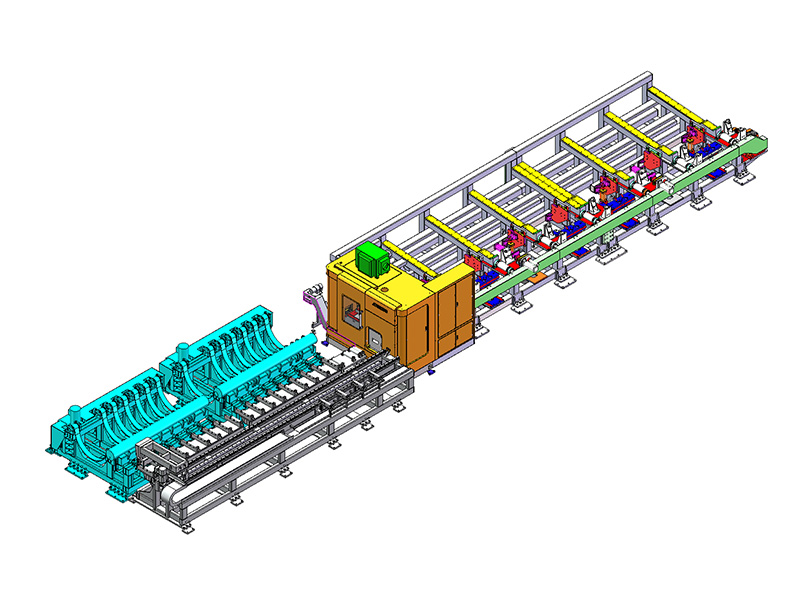
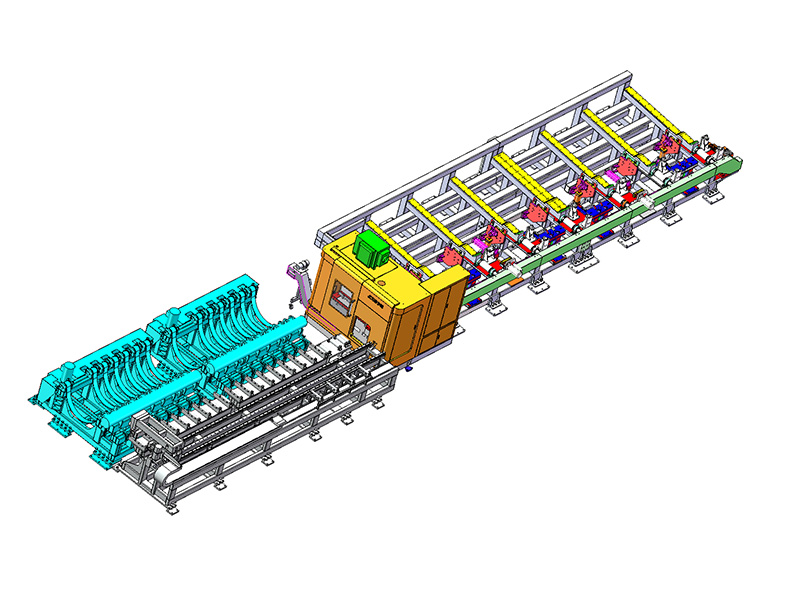
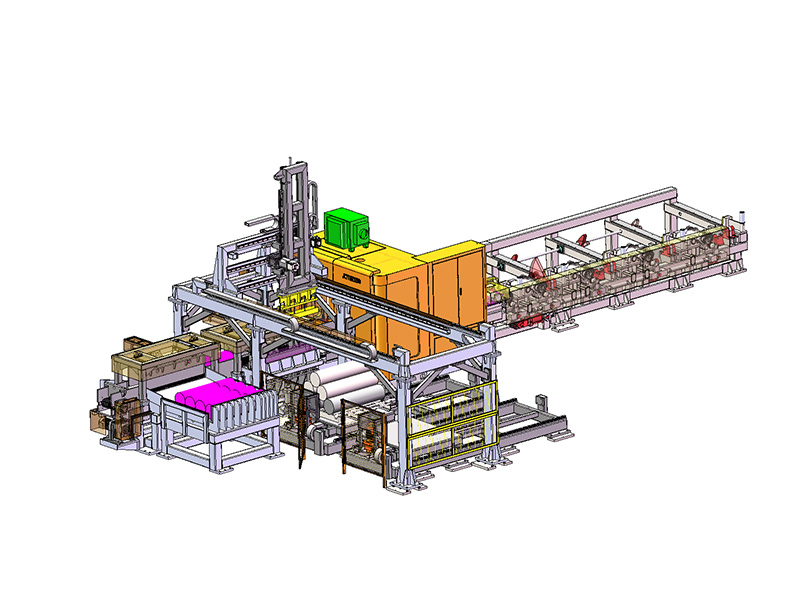
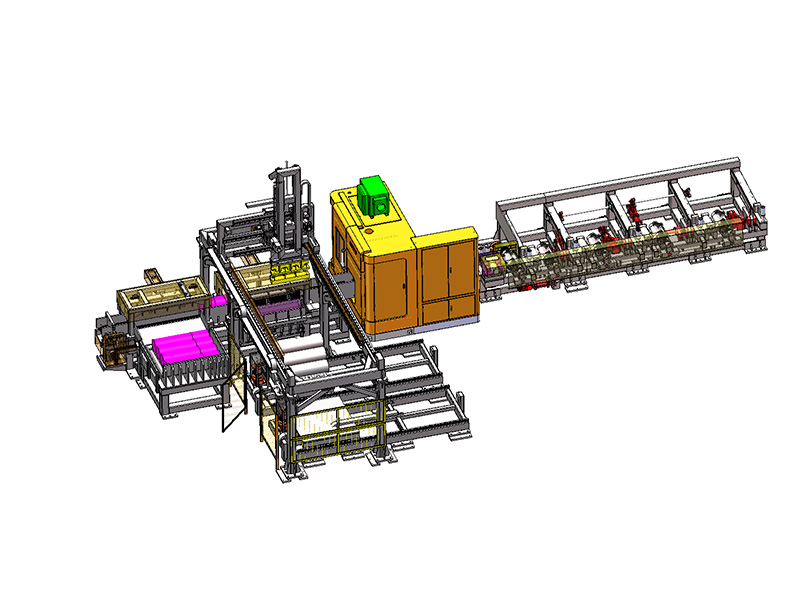
What makes this production line "intelligent" compared to traditional blanking systems?
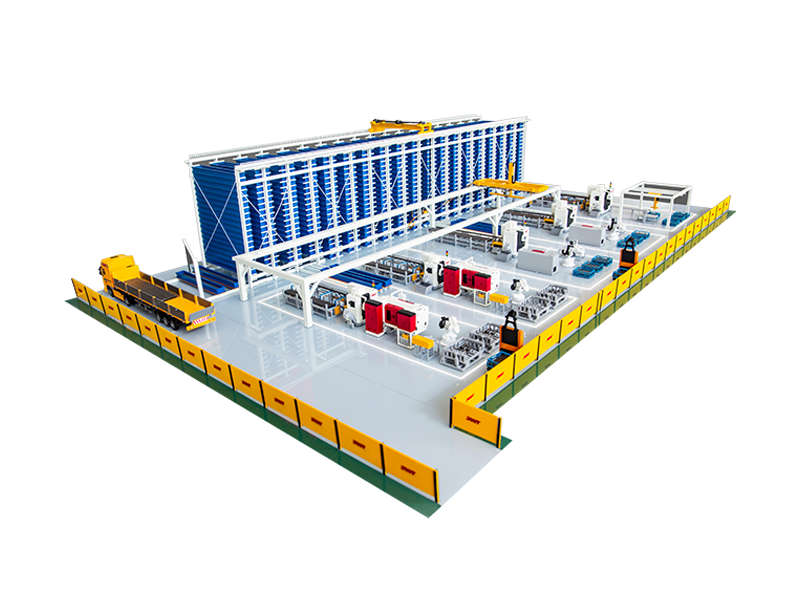
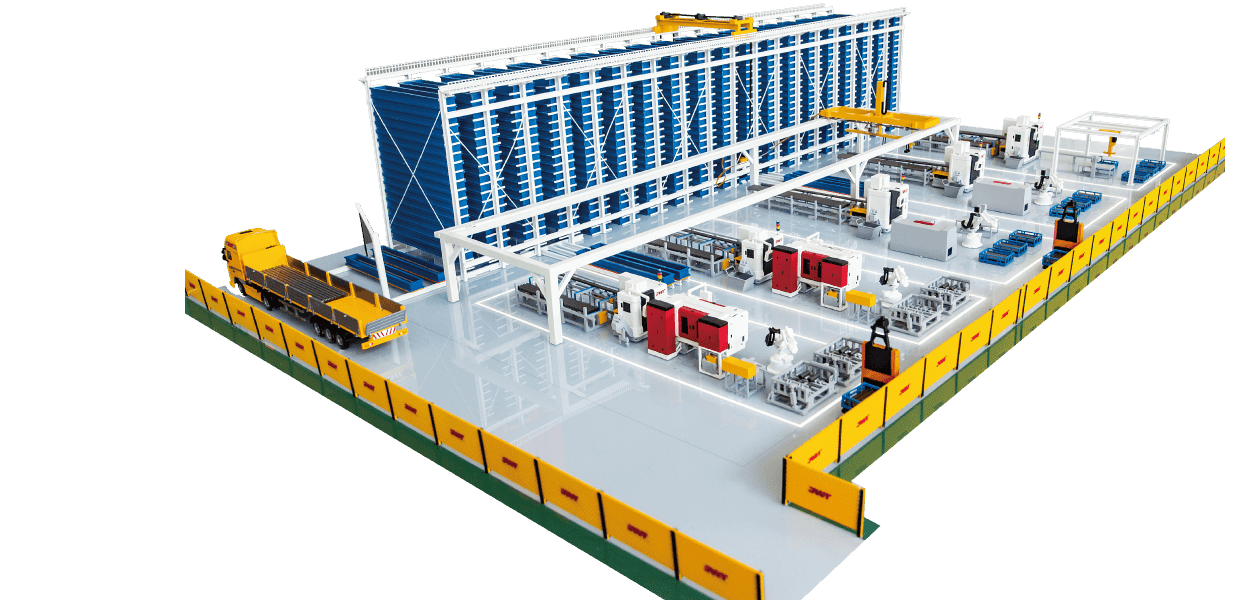
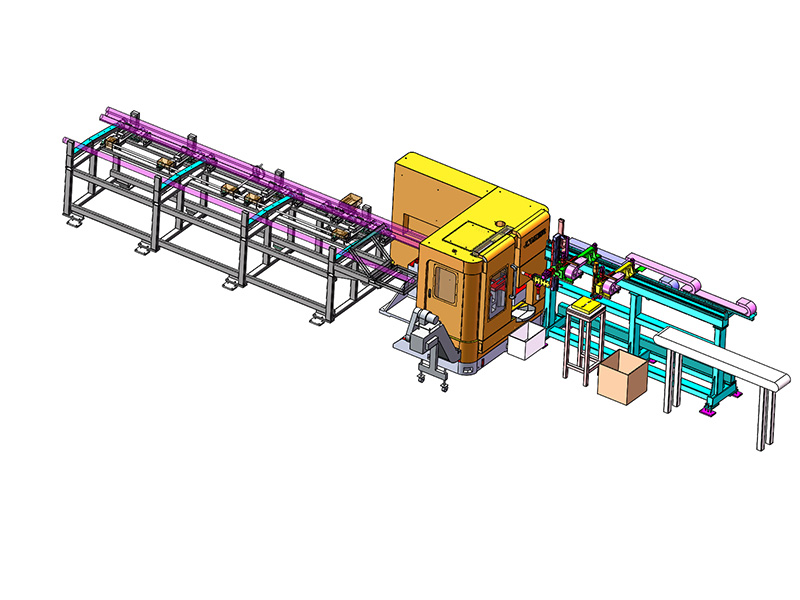
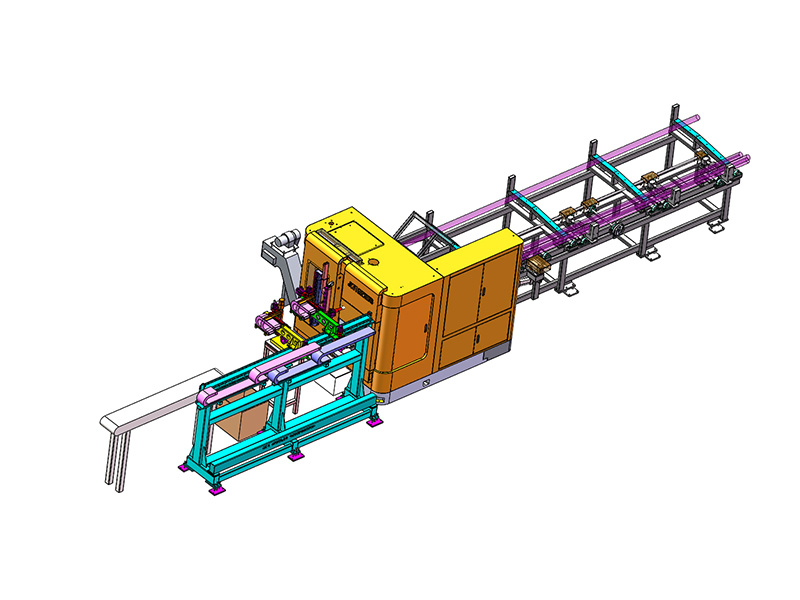
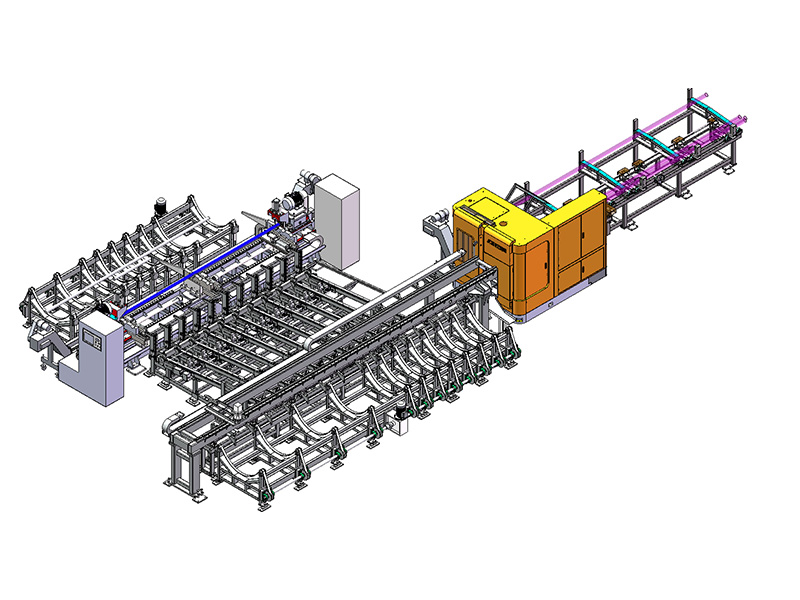
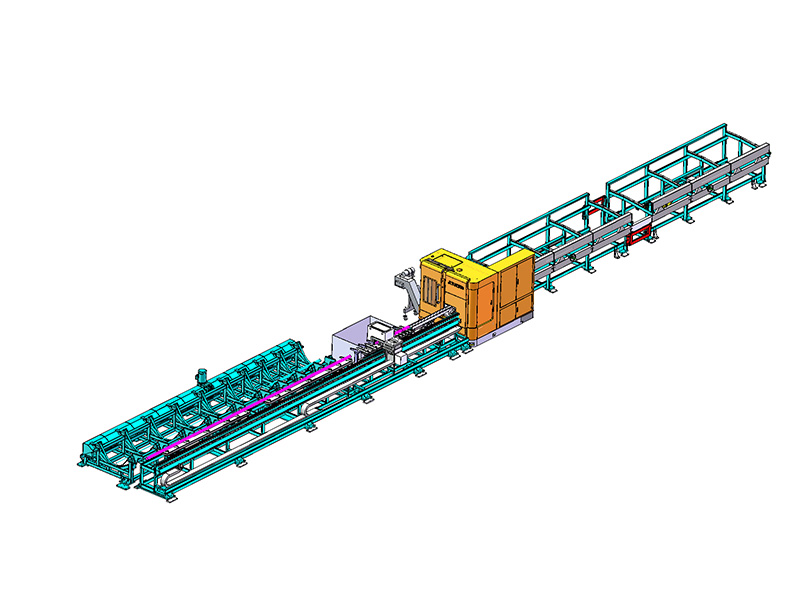
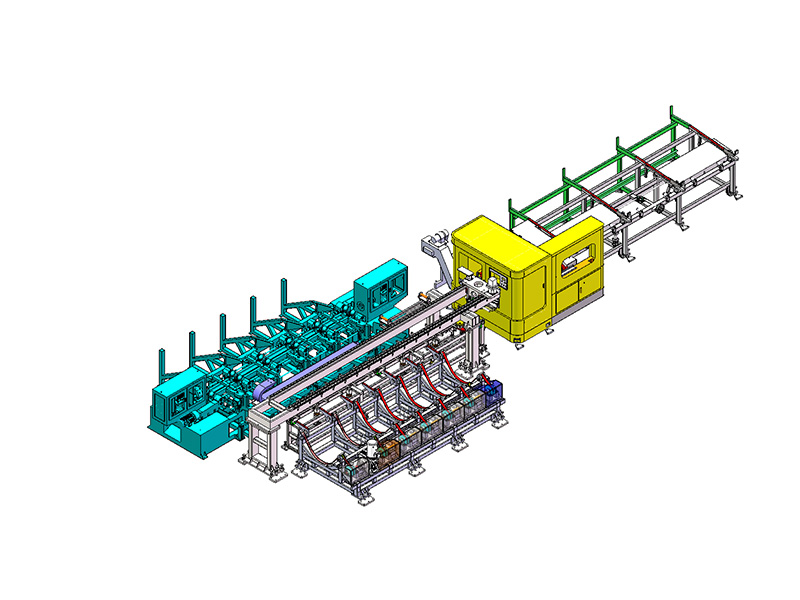
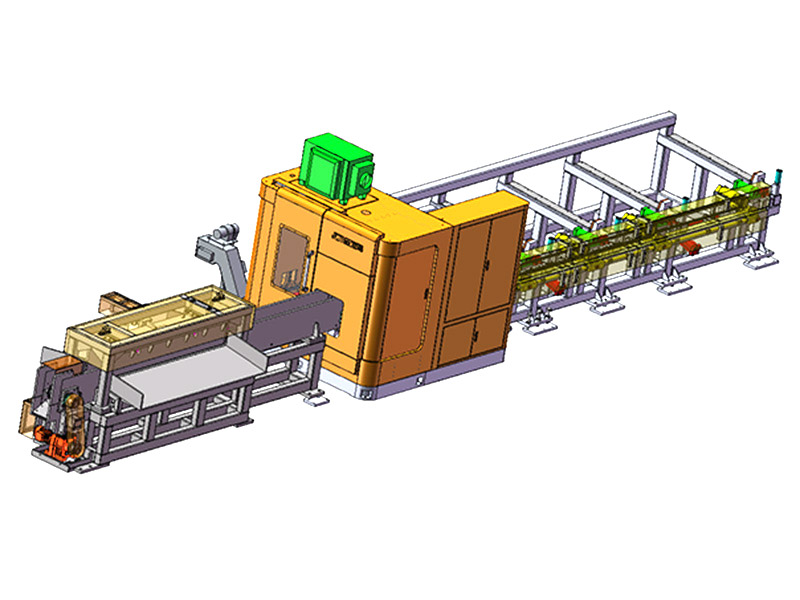
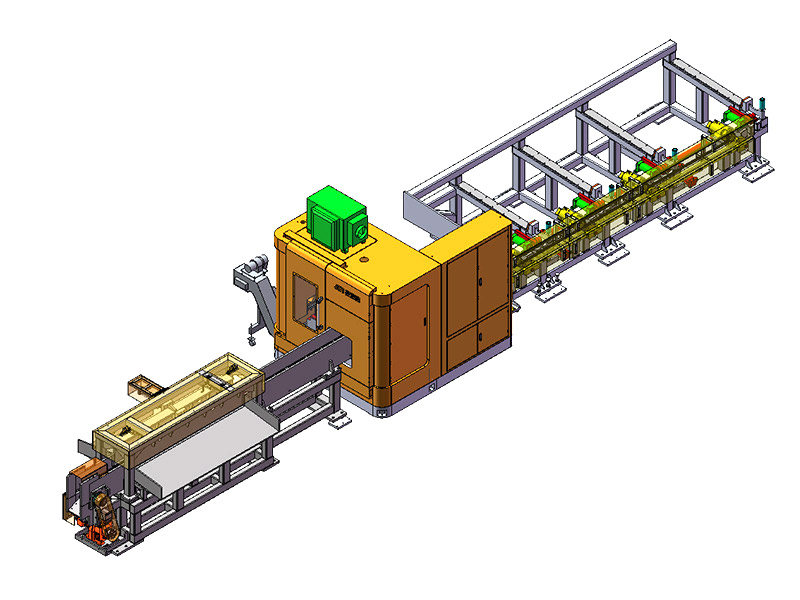
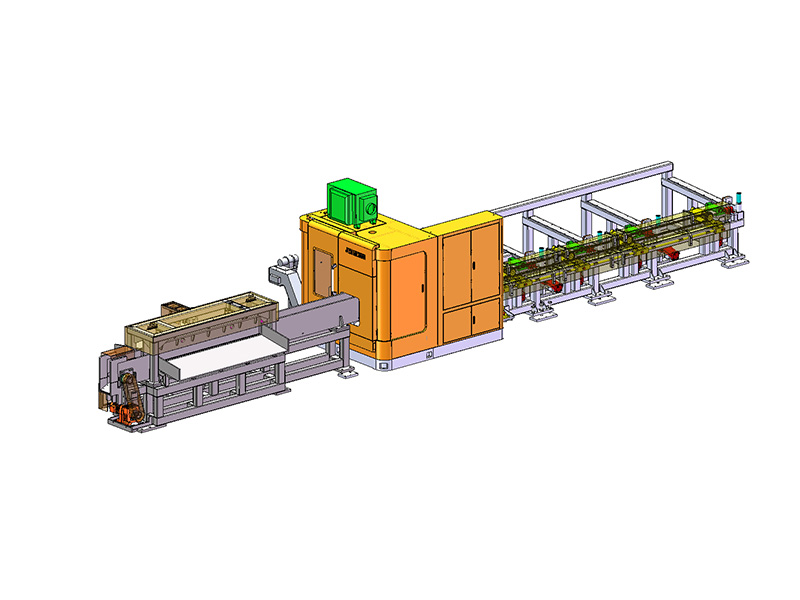
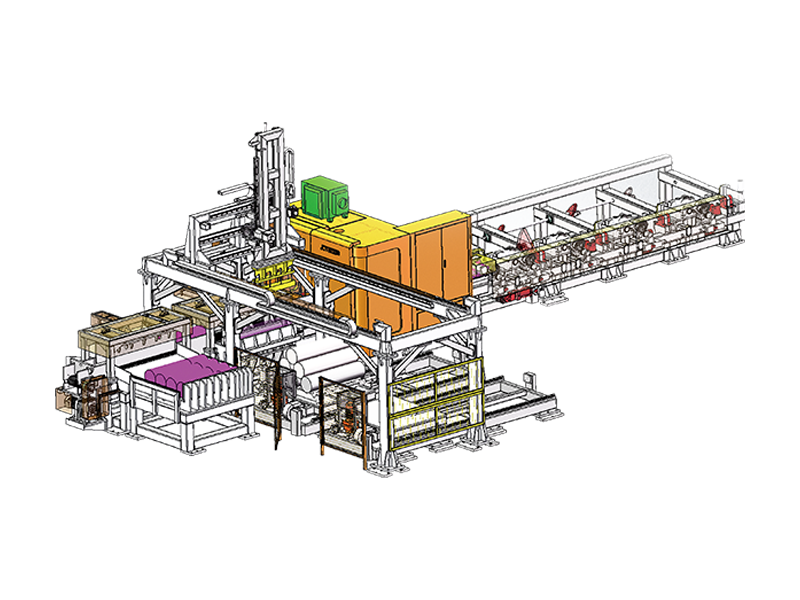
The term "intelligent" in the context of an Intelligent Storage Blanking Production Line typically refers to several key features and capabilities that differentiate it from traditional blanking systems:
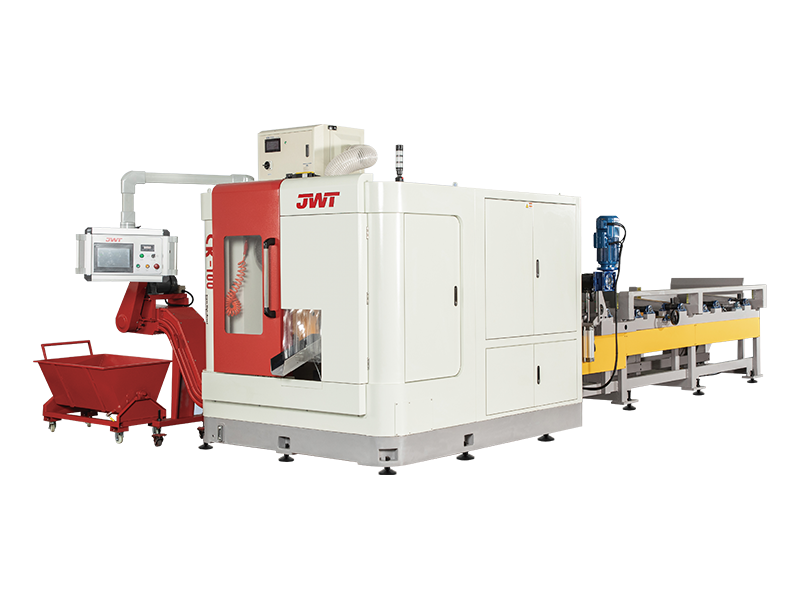
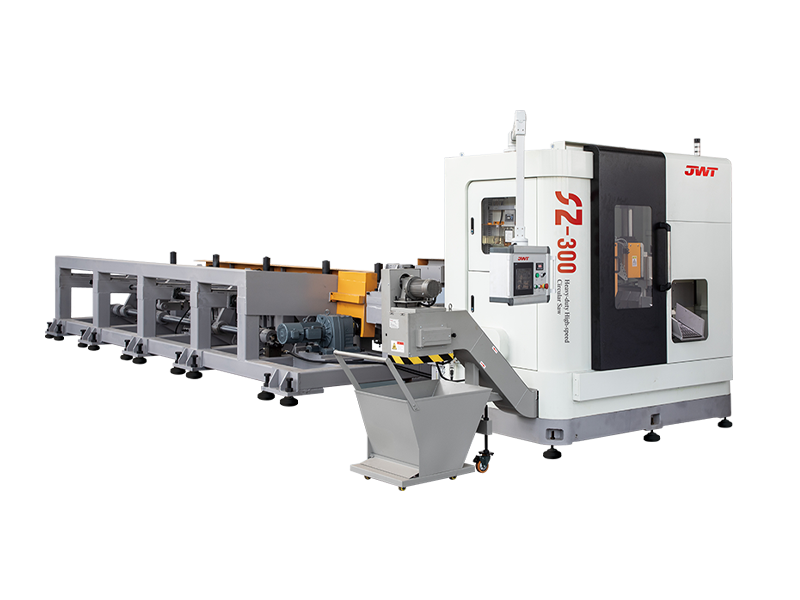
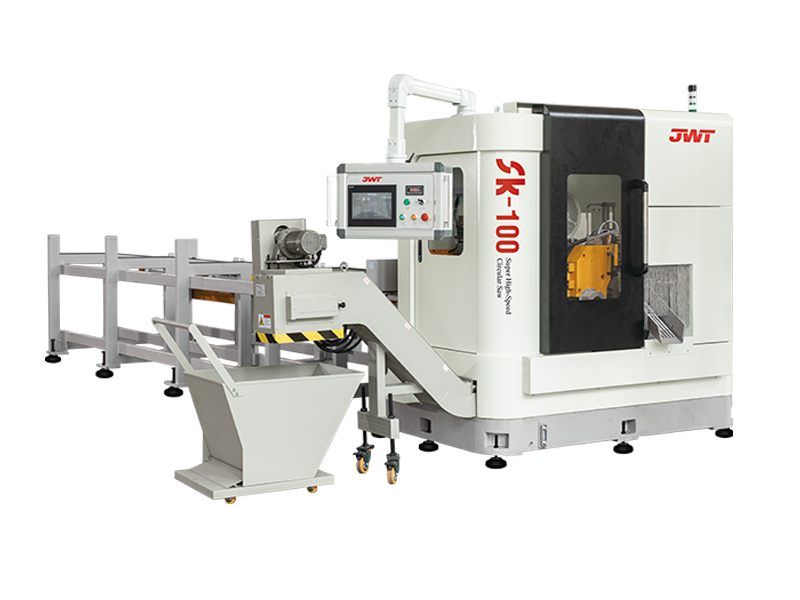
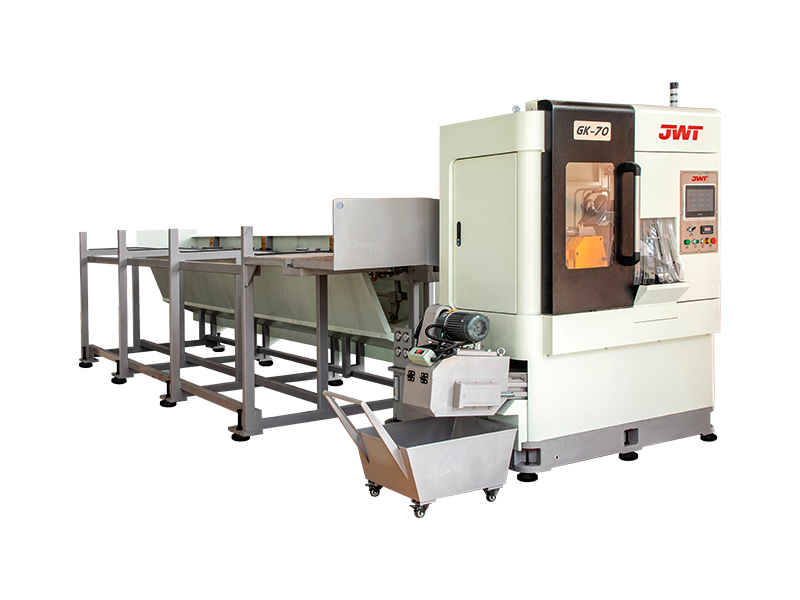
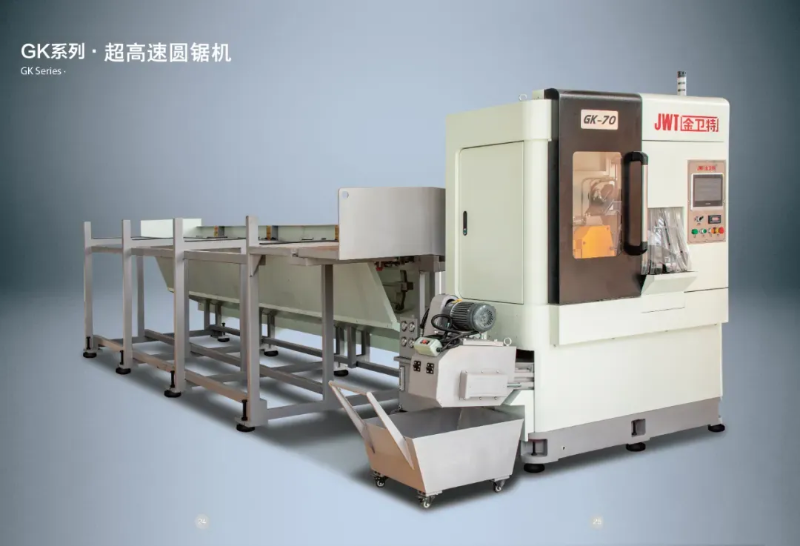
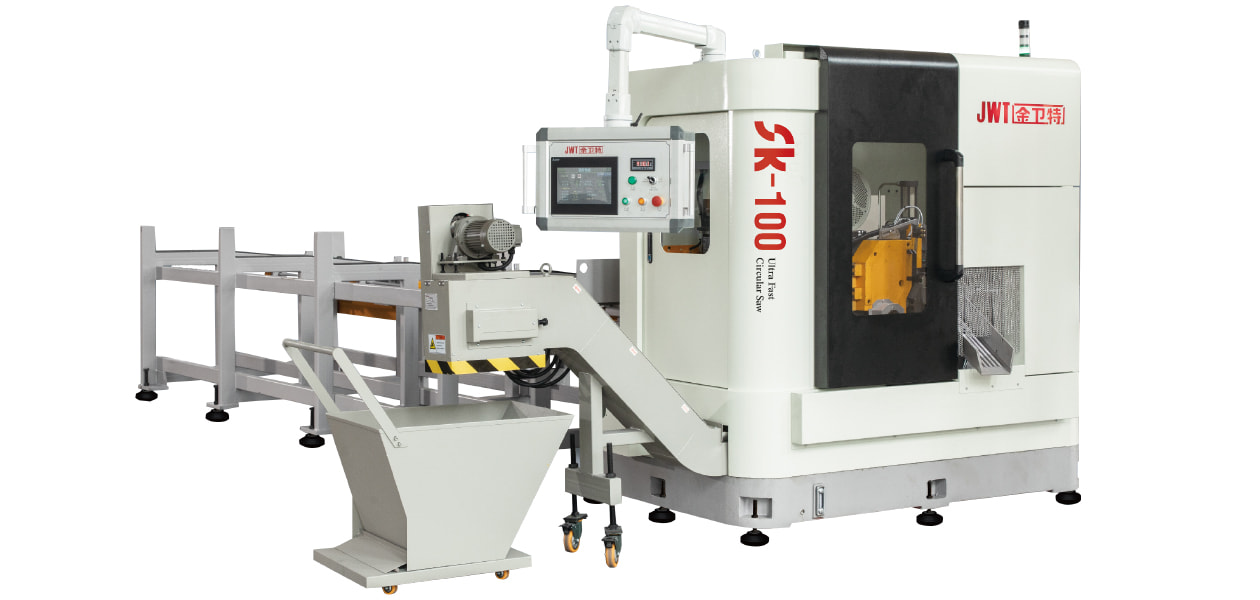
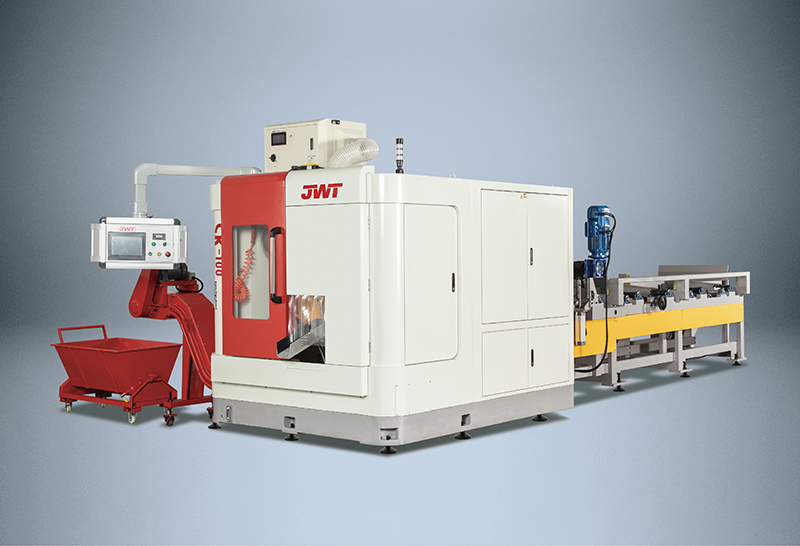
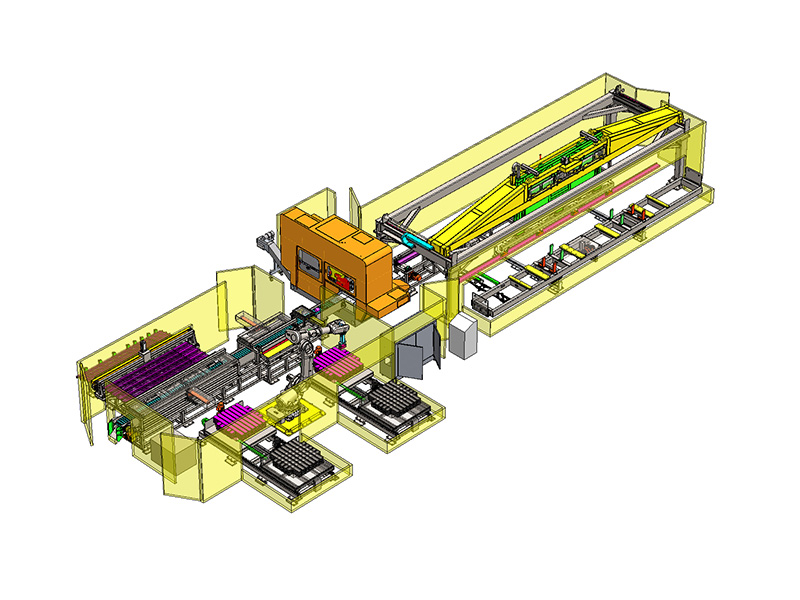
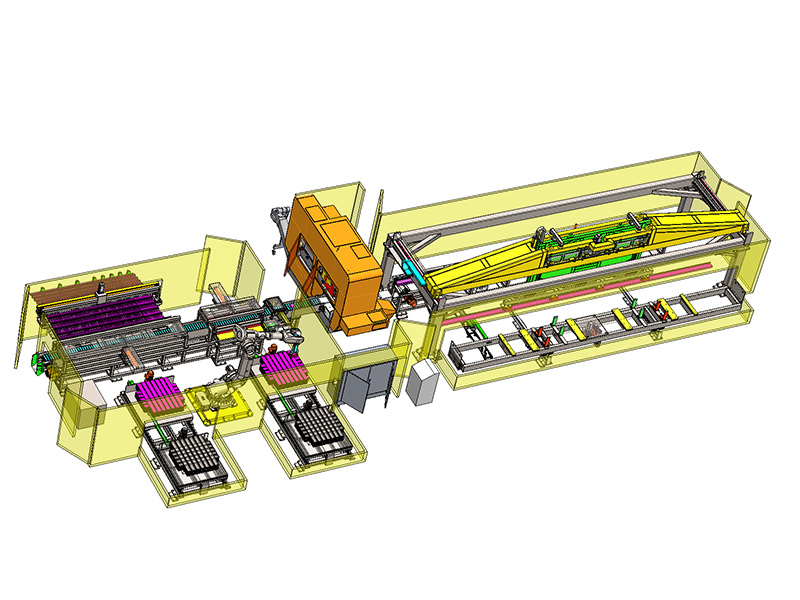
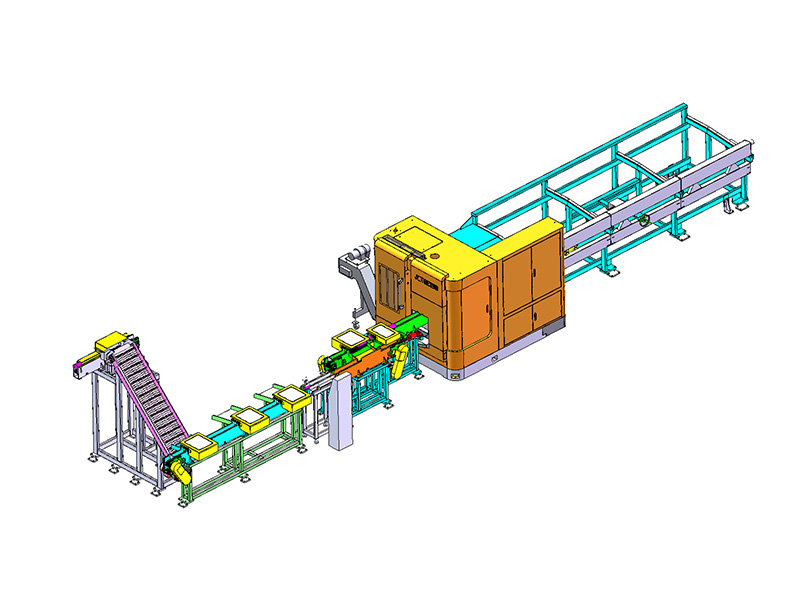
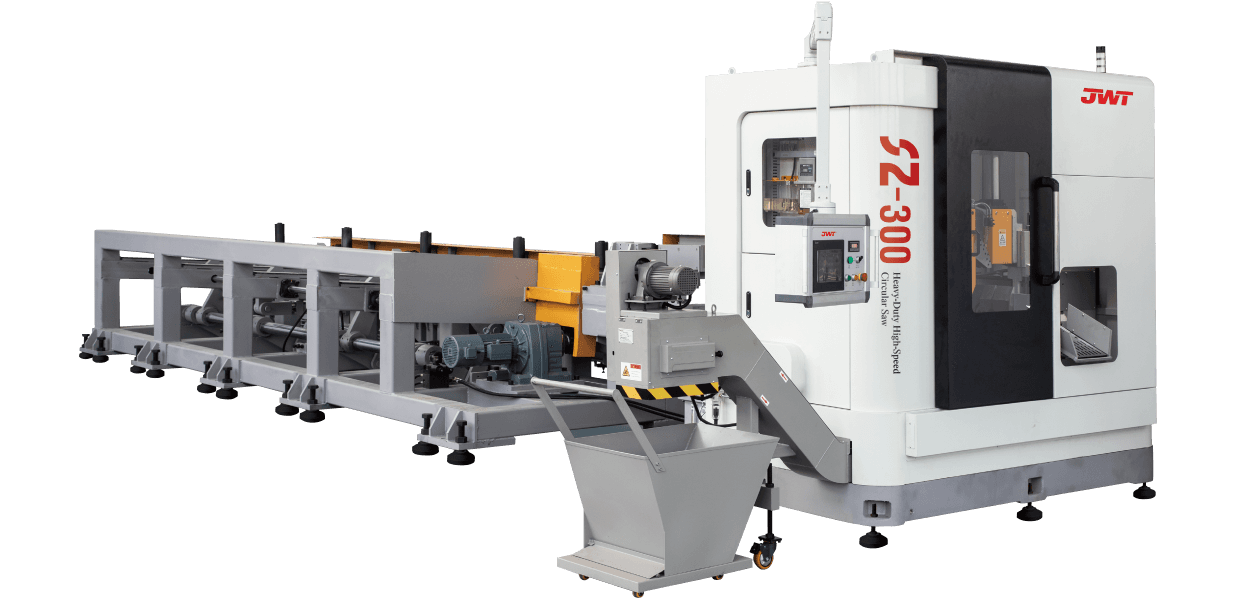
Automation and Robotics: Intelligent production lines often integrate advanced robotics and automation technologies. This includes robotic arms for material handling, automated loading and unloading of sheets, and even robotic quality inspection systems. This level of automation reduces manual intervention, minimizes human error, and speeds up the overall production process.
Sensors and IoT Integration: Intelligent production lines are equipped with a network of sensors that collect real-time data on various parameters such as temperature, humidity, material thickness, and machine performance. This data is often integrated into an IoT (Internet of Things) framework, allowing for remote monitoring, proactive maintenance scheduling, and data-driven decision-making.
Flexibility and Customization: Unlike traditional blanking systems that may have limited flexibility in handling different materials or sheet sizes, intelligent production lines are designed for versatility. They can quickly adjust settings and tooling configurations to accommodate different production requirements, thereby reducing setup times and increasing overall throughput.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability: Intelligent production lines are often engineered with energy-efficient components and processes. They may incorporate energy-saving features such as regenerative braking on motors, optimized power usage during idle periods, and intelligent shutdown protocols. This focus on sustainability aligns with global initiatives for reducing carbon footprint and improving resource efficiency.
Adaptability to Industry 4.0 Standards: Intelligent production lines are designed to meet the principles of Industry 4.0, which emphasize interconnectedness, information transparency, and decentralized decision-making. They can communicate seamlessly with other parts of the manufacturing ecosystem, such as suppliers and customers, to optimize supply chain logistics and enhance overall production efficiency.



 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский